Setting up your own VPN infrastructure has become increasingly critical for businesses seeking secure remote access to their on-premises resources. With cloud adoption accelerating and remote work becoming the norm, establishing a reliable OpenVPN server on AWS EC2 provides a cost-effective, scalable solution that bridges your on-premises network with cloud resources. This comprehensive guide will walk you through every step of creating a robust OpenVPN server implementation that ensures secure connectivity while maintaining enterprise-grade security standards.
Understanding OpenVPN and Its Strategic Benefits
OpenVPN stands as one of the most trusted and widely-adopted VPN protocols in the industry, offering unparalleled flexibility and security for enterprise networking needs. Unlike proprietary VPN solutions, OpenVPN is built on open-source foundations, providing transparency and continuous security improvements through community contributions. The protocol utilizes SSL/TLS encryption with 256-bit AES encryption, ensuring that all data transmitted through your VPN tunnel remains protected from potential threats.
Key Advantages of OpenVPN for Enterprise Use
Enhanced Security Architecture: OpenVPN implements multiple layers of security including certificate-based authentication, perfect forward secrecy, and support for various encryption algorithms. This multi-layered approach ensures that even if one security component is compromised, your network remains protected.
Cross-Platform Compatibility: One of OpenVPN’s greatest strengths lies in its universal compatibility across operating systems including Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android. This flexibility ensures that your remote workforce can maintain secure connections regardless of their preferred devices or platforms.
Scalability and Performance: When deployed on AWS EC2, OpenVPN can scale horizontally to accommodate growing user bases and increasing connection demands. The combination of AWS’s robust infrastructure and OpenVPN’s efficient protocol design delivers consistent performance even under heavy loads.
AWS EC2: The Ideal Platform for OpenVPN Deployment
Amazon EC2 provides the perfect foundation for hosting OpenVPN servers, offering several compelling advantages over traditional on-premises VPN solutions. The cloud-based approach eliminates the need for dedicated hardware while providing enterprise-grade reliability and performance.
EC2 Instance Selection Strategy
Choosing the appropriate EC2 instance type is crucial for optimal OpenVPN performance. For small to medium deployments (5-25 concurrent users), a t3.micro or t3.small instance typically provides sufficient resources. These instances offer burstable performance capabilities, allowing for occasional traffic spikes while maintaining cost efficiency.
For larger deployments or environments requiring consistent high-performance networking, consider m5.large or m6i.large instances. These instance types provide dedicated network bandwidth and enhanced networking capabilities, ensuring reliable performance for mission-critical VPN connections.
Cost Optimization Considerations
AWS’s pay-as-you-go pricing model makes OpenVPN deployment extremely cost-effective compared to traditional hardware-based solutions. A t3.micro instance running 24/7 costs approximately $8-12 per month, while providing VPN services for multiple users. This represents significant savings compared to dedicated VPN appliances that can cost thousands of dollars upfront.
Comprehensive Pre-Deployment Planning
Network Architecture Design
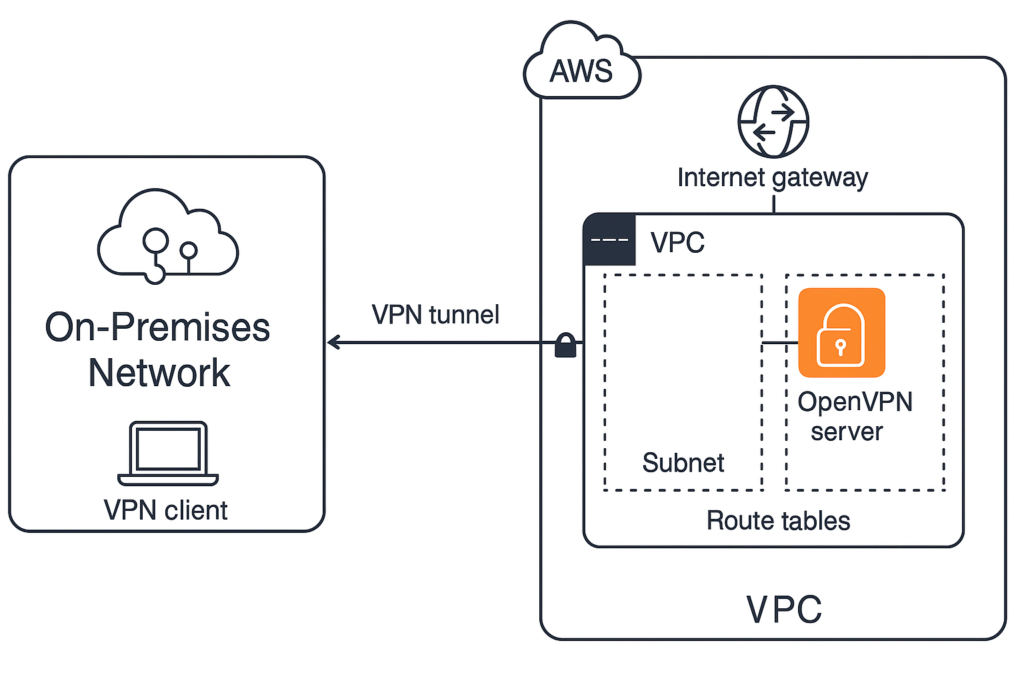
Before launching your OpenVPN server, careful network planning ensures optimal performance and security. Your AWS VPC should be configured with both public and private subnets, allowing the OpenVPN server to act as a secure gateway between external clients and internal resources.
VPC Configuration Best Practices:
- Use non-overlapping CIDR blocks between your on-premises network and AWS VPC
- Implement multiple Availability Zones for high availability
- Configure separate subnets for DMZ and internal resources
- Plan IP address allocation to avoid conflicts with existing infrastructure
Security Group Configuration Strategy
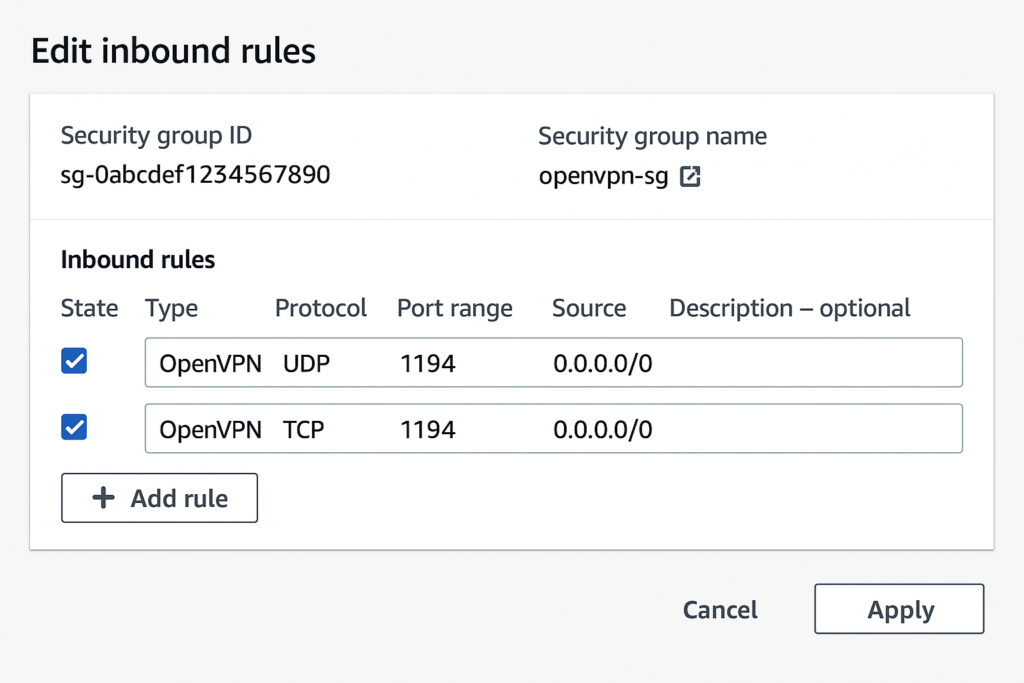
AWS Security Groups function as virtual firewalls, controlling inbound and outbound traffic to your OpenVPN server. Proper configuration is essential for both security and functionality.
Essential Security Group Rules:
- SSH (TCP 22): Restrict to your management IP addresses only
- OpenVPN (UDP 1194): Allow from anywhere (0.0.0.0/0) for client connections
- HTTPS (TCP 443): For web-based management interface access
- ICMP: Enable for network troubleshooting and connectivity testing
Step-by-Step OpenVPN Server Installation
Phase 1: EC2 Instance Preparation
Begin by launching a new EC2 instance with the following specifications:
- AMI Selection: Choose Amazon Linux 2 AMI for optimal compatibility and performance
- Instance Type: Select based on your expected user load (t3.micro for testing, t3.small+ for production)
- Key Pair: Create or select an existing SSH key pair for secure access
- VPC Placement: Deploy in your public subnet for internet accessibility
- Elastic IP: Assign a static IP address to ensure consistent connectivity
Phase 2: System Updates and Package Installation
Connect to your instance via SSH and perform initial system preparation:
# Update system packages sudo yum update -y # Install EPEL repository for additional packages sudo amazon-linux-extras install epel -y # Install OpenVPN and Easy-RSA for certificate management sudo yum install openvpn easy-rsa -y
Phase 3: Certificate Authority (CA) Setup
OpenVPN requires a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) for secure certificate-based authentication. This process creates the necessary certificates and keys:
# Create CA directory mkdir -p ~/openvpn-ca cd ~/openvpn-ca # Copy Easy-RSA scripts cp -r /usr/share/easy-rsa/3/* ./ # Initialize PKI ./easyrsa init-pki # Build Certificate Authority ./easyrsa build-ca nopass # Generate server certificate and key ./easyrsa gen-req server nopass ./easyrsa sign-req server server # Generate Diffie-Hellman parameters for perfect forward secrecy ./easyrsa gen-dh # Generate TLS authentication key openvpn --genkey --secret ta.key
Phase 4: Server Configuration
Create the OpenVPN server configuration file at /etc/openvpn/server.conf:
# Network settings port 1194 proto udp dev tun # SSL/TLS root certificate, certificate, private key, and DH parameters ca /home/ec2-user/openvpn-ca/pki/ca.crt cert /home/ec2-user/openvpn-ca/pki/issued/server.crt key /home/ec2-user/openvpn-ca/pki/private/server.key dh /home/ec2-user/openvpn-ca/pki/dh.pem # Network topology and IP allocation server 10.8.0.0 255.255.255.0 topology subnet # Enable client-to-client communication client-to-client # Maintain client routing table client-config-dir ccd route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 # TLS authentication tls-auth /home/ec2-user/openvpn-ca/ta.key 0 # Security enhancements cipher AES-256-GCM auth SHA256 compress lz4-v2 push "compress lz4-v2" # User and group privileges user nobody group nobody # Persistence options persist-key persist-tun # Logging status openvpn-status.log log-append openvpn.log verb 3 explicit-exit-notify 1
Phase 5: System Service Configuration
Enable and start the OpenVPN service:
# Copy certificates to OpenVPN directory sudo cp ~/openvpn-ca/pki/ca.crt /etc/openvpn/ sudo cp ~/openvpn-ca/pki/issued/server.crt /etc/openvpn/ sudo cp ~/openvpn-ca/pki/private/server.key /etc/openvpn/ sudo cp ~/openvpn-ca/pki/dh.pem /etc/openvpn/ sudo cp ~/openvpn-ca/ta.key /etc/openvpn/ # Set appropriate permissions sudo chmod 600 /etc/openvpn/server.key sudo chmod 600 /etc/openvpn/ta.key # Enable IP forwarding echo 'net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1' | sudo tee -a /etc/sysctl.conf sudo sysctl -p # Configure firewall rules sudo iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 10.8.0.0/24 -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE sudo iptables -A INPUT -i tun+ -j ACCEPT sudo iptables -A FORWARD -i tun+ -j ACCEPT sudo iptables -A FORWARD -i tun+ -o eth0 -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT sudo iptables -A FORWARD -i eth0 -o tun+ -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Start and enable OpenVPN service sudo systemctl start openvpn@server sudo systemctl enable openvpn@server
Client Certificate Generation and Configuration
Creating Client Certificates
For each client that needs VPN access, generate individual certificates:
cd ~/openvpn-ca # Generate client certificate request ./easyrsa gen-req client1 nopass # Sign the client certificate ./easyrsa sign-req client client1 # Repeat for additional clients (client2, client3, etc.)
Client Configuration File Template
Create a client configuration template (client.ovpn):
client dev tun proto udp remote YOUR_EC2_PUBLIC_IP 1194 resolv-retry infinite nobind persist-key persist-tun remote-cert-tls server cipher AES-256-GCM auth SHA256 compress lz4-v2 verb 3 # Inline certificates (more secure than separate files) <ca> -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- [Insert CA certificate content here] -----END CERTIFICATE----- </ca> <cert> -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- [Insert client certificate content here] -----END CERTIFICATE----- </cert> <key> -----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY----- [Insert client private key content here] -----END PRIVATE KEY----- </key> <tls-auth> -----BEGIN OpenVPN Static key V1----- [Insert TLS authentication key content here] -----END OpenVPN Static key V1----- </tls-auth> key-direction 1
Advanced OpenVPN Use Cases and Scenarios
Site-to-Site Connectivity
OpenVPN excels in creating secure site-to-site connections between your on-premises infrastructure and AWS resources. This configuration allows entire networks to communicate securely as if they were on the same local network.
Configuration for Site-to-Site VPN:
- Configure static routing between network segments
- Implement redundant connections for high availability
- Use certificate-based authentication for enhanced security
- Monitor bandwidth utilization and connection health
Remote Workforce Access
In today’s distributed work environment, OpenVPN provides secure access to corporate resources for remote employees. The solution supports various authentication methods including LDAP integration, multi-factor authentication, and single sign-on capabilities.
Enterprise Remote Access Features:
- Split Tunneling: Route only corporate traffic through VPN while allowing direct internet access for other applications
- User Access Control: Implement granular permissions based on user roles and responsibilities
- Device Compliance: Ensure connecting devices meet security requirements
- Session Monitoring: Track user activity and connection patterns for security compliance
IoT Device Connectivity
OpenVPN’s lightweight footprint makes it ideal for securing IoT device communications. Whether connecting sensors, monitoring equipment, or industrial control systems, OpenVPN provides encrypted channels that protect sensitive operational data.
Performance Optimization and Monitoring
Instance Performance Tuning
Optimize your EC2 instance for maximum OpenVPN performance:
# Increase network buffer sizes echo 'net.core.rmem_max = 26214400' | sudo tee -a /etc/sysctl.conf echo 'net.core.rmem_default = 26214400' | sudo tee -a /etc/sysctl.conf echo 'net.core.wmem_max = 26214400' | sudo tee -a /etc/sysctl.conf echo 'net.core.wmem_default = 26214400' | sudo tee -a /etc/sysctl.conf # Optimize TCP settings echo 'net.ipv4.tcp_rmem = 4096 65536 26214400' | sudo tee -a /etc/sysctl.conf echo 'net.ipv4.tcp_wmem = 4096 65536 26214400' | sudo tee -a /etc/sysctl.conf # Apply changes sudo sysctl -p
Connection Monitoring and Analytics
Implement comprehensive monitoring to track VPN performance and user activity:
# Monitor active connections sudo systemctl status openvpn@server # View connection logs sudo tail -f /var/log/openvpn.log # Check connected clients sudo cat /etc/openvpn/openvpn-status.log
Troubleshooting Common Issues and Solutions
Connection Failures
- Verify certificate validity and expiration dates
- Check system time synchronization between server and clients
- Ensure firewall rules allow OpenVPN traffic on UDP port 1194
Authentication Problems:
- Validate certificate chain integrity
- Confirm client certificate hasn’t been revoked
- Check OpenVPN server logs for specific error messages
Performance Issues
- Monitor CPU utilization on EC2 instance
- Consider upgrading to instances with enhanced networking
- Implement connection pooling for high-traffic scenarios
- Optimize MTU settings for your network environment
Network Connectivity Problems
- Verify IP forwarding is enabled on the server
- Check routing tables on both server and client sides
- Ensure no IP address conflicts between networks
- Validate security group and NACL configurations
Also Read – How to Set Up a Private VPN for Your Organization
Security Best Practices and Hardening
Certificate Management
Implement robust certificate lifecycle management:
- Use strong key sizes (minimum 2048-bit RSA or 256-bit ECC)
- Implement certificate rotation policies
- Maintain secure certificate storage and backup procedures
- Monitor certificate expiration dates and plan renewals
Access Control Implementation
Deploy granular access controls to minimize security risks:
- Implement least-privilege access principles
- Use client-specific configuration files for granular control
- Enable client certificate revocation capabilities
- Monitor and log all VPN access attempts
Network Segmentation
Isolate VPN traffic from critical infrastructure:
- Use dedicated subnets for VPN clients
- Implement network access control lists (NACLs)
- Deploy intrusion detection systems (IDS)
- Regular security assessments and penetration testing
Cost Optimization Strategies
Right-Sizing Your Infrastructure
Choose optimal EC2 instance types based on actual usage patterns:
- Start with smaller instances and scale up as needed
- Monitor CPU, memory, and network utilization metrics
- Consider reserved instances for long-term deployments
- Implement auto-scaling for variable workloads
Bandwidth Management
Optimize data transfer costs through intelligent routing:
- Implement traffic shaping to prioritize critical applications
- Use CloudWatch metrics to monitor data transfer patterns
- Consider AWS Direct Connect for high-volume scenarios
- Implement compression to reduce bandwidth usage
Integration with AWS Services
CloudWatch Integration
Leverage AWS CloudWatch for comprehensive monitoring:
- Set up custom metrics for connection counts and bandwidth usage
- Configure alarms for service availability and performance thresholds
- Create dashboards for real-time visibility into VPN operations
- Implement automated responses to common issues
AWS Directory Service Integration
Connect OpenVPN with AWS Directory Service for centralized authentication:
- Integrate with existing Active Directory infrastructure
- Implement single sign-on (SSO) capabilities
- Centralize user management and authentication policies
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for enhanced security
Disaster Recovery and High Availability
Multi-AZ Deployment
Implement high availability across multiple Availability Zones:
- Deploy OpenVPN servers in multiple AZs
- Configure load balancing for client connections
- Implement automated failover mechanisms
- Maintain synchronized certificate stores across instances
Backup and Recovery Procedures
Establish comprehensive backup strategies:
- Regular snapshots of EBS volumes containing certificates and configurations
- Automated backup of PKI certificate authority data
- Document recovery procedures and test them regularly
- Implement version control for configuration files
Conclusion: Building a Robust OpenVPN Infrastructure
Implementing OpenVPN on AWS EC2 provides organizations with a powerful, scalable, and cost-effective solution for secure remote access. The combination of OpenVPN’s proven security architecture and AWS’s robust cloud infrastructure creates a foundation that can grow with your organization’s needs while maintaining enterprise-grade security standards.
The investment in properly configured OpenVPN infrastructure pays dividends through improved security posture, enhanced remote work capabilities, and reduced reliance on expensive proprietary VPN solutions. By following the comprehensive guidelines outlined in this guide, organizations can deploy a production-ready OpenVPN server that provides secure, reliable connectivity for years to come.
Success with OpenVPN on AWS requires ongoing attention to security updates, performance monitoring, and capacity planning. Regular reviews of access patterns, security configurations, and performance metrics ensure that your VPN infrastructure continues to meet evolving business needs while maintaining the highest security standards.
Whether you’re supporting a small remote team or a large distributed workforce, OpenVPN on AWS EC2 provides the flexibility, security, and scalability needed to support modern business operations. The open-source nature of OpenVPN, combined with AWS’s enterprise-grade infrastructure, creates a winning combination that delivers both immediate value and long-term strategic advantages.

