Picture this: You’re reviewing your AWS bill, and the numbers make you wince. You’re not alone – many organizations struggle with cloud costs, especially when running workloads on-demand. But there’s good news: AWS offers two powerful cost-saving options – Savings Plans and Reserved Instances (RIs). Let’s dive deep into these options and help you make the right choice for your organization.
The Basics: Understanding Your Options
What are Reserved Instances?
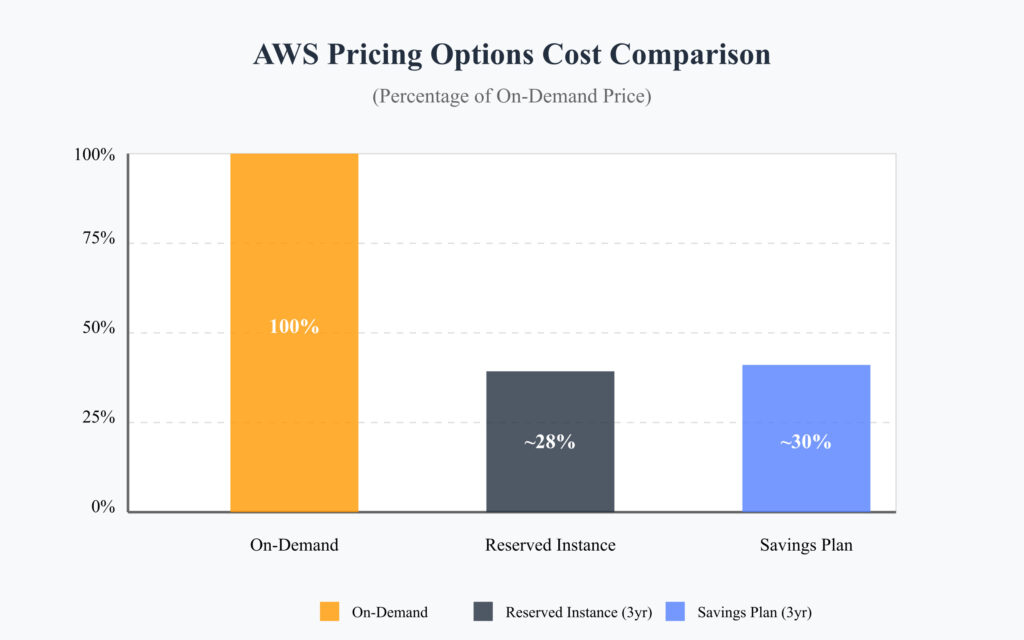
Think of Reserved Instances as bulk-buying your favorite products at a wholesale price. When you purchase RIs, you’re committing to use a specific instance type in a particular region for a set period (1 or 3 years). In return, AWS offers significant discounts – up to 72% compared to on-demand pricing.
What are Savings Plans?
Savings Plans are the newer, more flexible cousin of RIs. Instead of committing to a specific instance type, you’re committing to spend a certain amount per hour on compute usage. It’s like having a prepaid phone plan – you commit to spending a minimum amount, but you have flexibility in how you use it.
Deep Dive: Key Differences and Benefits
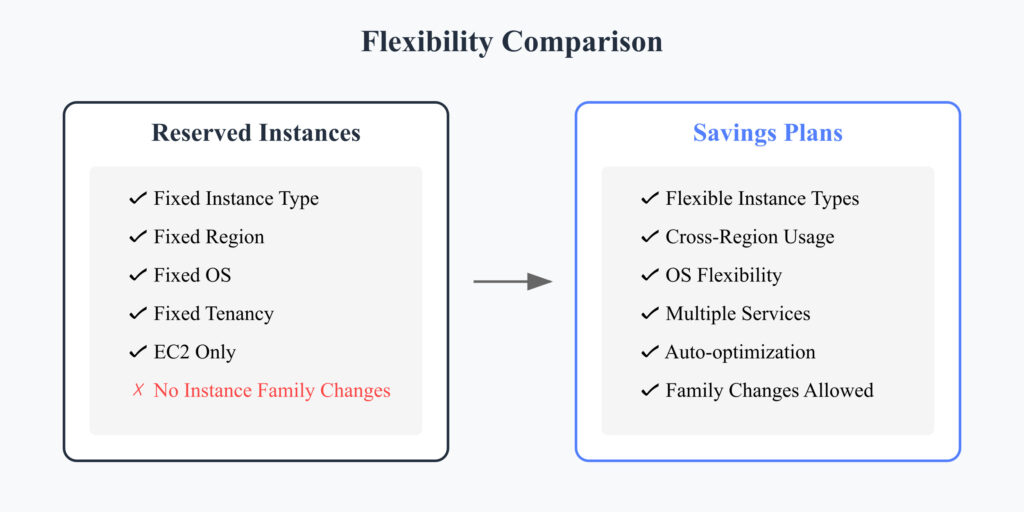
Flexibility
Reserved Instances:
- Instance type locked
- Region locked (unless you purchase Regional RIs)
- OS locked
- Tenancy locked
Let’s consider a scenario: You’ve purchased a t3.large RI for your application. Six months later, you realize you need more computing power. With RIs, you’re stuck with that instance type unless you modify or sell it on the AWS RI Marketplace.
Savings Plans:
- Flexible across instance types
- Flexible across regions (for Compute Savings Plans)
- Flexible across OS
- Works with Lambda and Fargate
Imagine you’re running a dynamic e-commerce platform. During the day, you need compute-optimized instances for handling transactions, while at night, you switch to memory-optimized instances for data analytics. Savings Plans accommodate this flexibility without any manual intervention.
Cost Savings
Both options offer significant savings, but the approach differs:
Reserved Instances:
- Up to 72% savings with All Upfront payment
- Predictable instance-specific pricing
- Potentially deeper discounts for specific instance types
Savings Plans:
- Up to 72% savings with All Upfront payment
- More consistent savings across different services
- Automatic optimization of spending
Real-world Scenario: Growing Startup
Let’s follow a startup’s journey to understand these differences better:
Phase 1: Initial Setup
- Workload: Web application with predictable traffic
- Choice: Reserved Instances
- Reasoning: Known instance types needed, predictable workload
- Savings: 65% with Partial Upfront payment
Phase 2: Rapid Growth
- Workload: Multiple applications, varying resource needs
- Choice: Compute Savings Plan
- Reasoning: Need flexibility to experiment with different instance types
- Savings: 66% while maintaining workload flexibility
Making the Right Choice
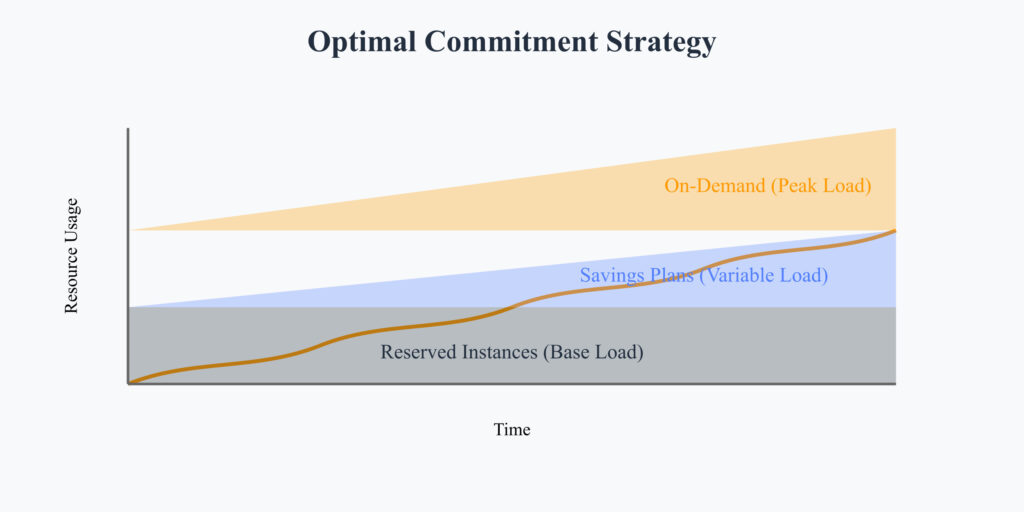
Consider these factors when deciding:
- Workload Predictability
- Static, predictable workloads → Reserved Instances
- Dynamic, evolving workloads → Savings Plans
- Management Overhead
- Reserved Instances require more active management
- Savings Plans offer automated optimization
- Commitment Level
- Both options require 1 or 3-year commitments
- Payment options: All Upfront, Partial Upfront, or No Upfront
Advanced Strategies and Tips
Hybrid Approach
Many organizations benefit from using both options:
Reserved Instances for: - Core infrastructure that doesn't change - Specific instance types with deep discounts - Regional capacity reservation needs Savings Plans for: - Variable workloads - Multiple AWS services (EC2, Lambda, Fargate) - Multi-region deployments
Cost Analysis Example
Let’s analyze a medium-sized application:
Current Setup:
- 10 t3.large instances running 24/7
- Monthly on-demand cost: $1,500
Option 1: Reserved Instances (3-year term)
- Upfront cost: $10,800
- Monthly cost: $300
- Total savings: 68%
Option 2: Compute Savings Plan (3-year term)
- Commitment: $450/month
- Flexibility to change instance types
- Total savings: 66%
Implementation Best Practices
- Start Small
Begin with a small commitment (25-30% of your workload) and gradually increase as you understand your usage patterns. - Regular Review
Set up monthly reviews of your commitment coverage and adjust as needed. - Use AWS Cost Explorer
Leverage AWS Cost Explorer’s recommendations for both RIs and Savings Plans. - Monitor and Adjust
Keep track of utilization rates and modify your strategy based on changing needs.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Over-commitment
Don’t commit to more than you need. Start conservative and scale up. - Ignoring Instance Family Changes
New instance types are regularly introduced. Don’t lock yourself into old technology with long-term RIs. - Missing Regional Opportunities
Consider regional pricing differences when making commitments.
Future Considerations
As AWS continues to evolve, keep these factors in mind:
- New Instance Types
AWS regularly introduces new instance types with better price-performance ratios. - Service Integration
Savings Plans might expand to cover more AWS services. - Pricing Changes
Stay informed about AWS pricing changes and new discount options.
Conclusion
Both Reserved Instances and Savings Plans offer substantial cost savings, but they serve different needs. RIs are perfect for stable, predictable workloads where you know exactly what instance types you need. Savings Plans offer more flexibility and are ideal for dynamic workloads or organizations that want simpler cost optimization.
The best approach often combines both options: use RIs for your stable base workload and Savings Plans for everything else. Remember to start small, monitor regularly, and adjust your strategy as your needs evolve.
By understanding these options and implementing them strategically, you can significantly reduce your AWS costs while maintaining the flexibility to grow and adapt your infrastructure as needed.
Also Read ECS to EKS Migration Guide
References
- AWS Pricing Overview
https://aws.amazon.com/pricing/
Comprehensive details about AWS services and pricing models. - AWS Savings Plans Documentation
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/savingsplans/
Official documentation on Savings Plans, including Compute and EC2 Instance Savings Plans. - AWS Reserved Instances FAQs
https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/pricing/reserved-instances/
In-depth FAQs about Reserved Instances and their usage. - AWS Cost Explorer
https://aws.amazon.com/aws-cost-management/aws-cost-explorer/
Tool to analyze cost trends and optimize usage with recommendations for RIs and Savings Plans. - AWS Well-Architected Framework – Cost Optimization
https://aws.amazon.com/architecture/well-architected/
Guidelines to align your architecture with cost optimization best practices. - AWS Blogs on Cost Management
https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/
Articles on real-world strategies and insights into managing AWS costs effectively. - AWS Marketplace for Reserved Instances
https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/ri-marketplace/
Platform to buy and sell unused Reserved Instances.

